ProgressBar#
The Gtk.ProgressBar is typically used to display the progress of a
long running operation. It provides a visual clue that processing is underway.
The Gtk.ProgressBar can be used in two different modes: percentage
mode and activity mode.
When an application can determine how much work needs to take place (e.g. read
a fixed number of bytes from a file) and can monitor its progress, it can use
the Gtk.ProgressBar in percentage mode and the user sees a growing
bar indicating the percentage of the work that has been completed.
In this mode, the application is required to set
Gtk.ProgressBar.props.fraction periodically to update the progress bar,
setting a float between 0 and 1 to provide the new percentage value.
When an application has no accurate way of knowing the amount of work to do, it
can use activity mode, which shows activity by a block moving back and forth
within the progress area. In this mode, the application is required to call
Gtk.ProgressBar.pulse() periodically to update the progress bar.
You can also choose the step size, with the
Gtk.ProgressBar.props.pulse_step property.
By default, Gtk.ProgressBar is horizontal and left-to-right, but you
can change it to a vertical progress bar by changing the value of
Gtk.ProgressBar.props.orientation.
Changing the direction the progress bar grows can be done using
Gtk.ProgressBar.props.inverted. Gtk.ProgressBar can also
contain text which can be set with Gtk.ProgressBar.props.text and
Gtk.ProgressBar.props.show_text.
Example#
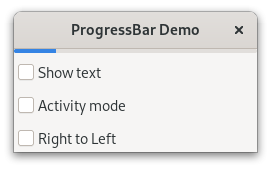
1import gi
2
3gi.require_version('Gtk', '4.0')
4from gi.repository import Gtk, GLib
5
6
7class ProgressBarWindow(Gtk.ApplicationWindow):
8 def __init__(self, **kargs):
9 super().__init__(**kargs, title='ProgressBar Demo')
10
11 vbox = Gtk.Box(orientation=Gtk.Orientation.VERTICAL, spacing=6)
12 self.set_child(vbox)
13
14 self.progressbar = Gtk.ProgressBar()
15 vbox.append(self.progressbar)
16
17 button = Gtk.CheckButton(label='Show text')
18 button.connect('toggled', self.on_show_text_toggled)
19 vbox.append(button)
20
21 button = Gtk.CheckButton(label='Activity mode')
22 button.connect('toggled', self.on_activity_mode_toggled)
23 vbox.append(button)
24
25 button = Gtk.CheckButton(label='Right to Left')
26 button.connect('toggled', self.on_right_to_left_toggled)
27 vbox.append(button)
28
29 self.timeout_id = GLib.timeout_add(50, self.on_timeout)
30 self.activity_mode = False
31
32 def on_show_text_toggled(self, button):
33 show_text = button.props.active
34 if show_text:
35 text = 'some text'
36 else:
37 text = None
38 self.progressbar.props.text = text
39 self.progressbar.props.show_text = show_text
40
41 def on_activity_mode_toggled(self, button):
42 self.activity_mode = button.props.active
43 if self.activity_mode:
44 self.progressbar.pulse()
45 else:
46 self.progressbar.props.fraction = 0.0
47
48 def on_right_to_left_toggled(self, button):
49 value = button.props.active
50 self.progressbar.props.inverted = value
51
52 def on_timeout(self):
53 '''
54 Update value on the progress bar
55 '''
56 if self.activity_mode:
57 self.progressbar.pulse()
58 else:
59 new_value = self.progressbar.props.fraction + 0.01
60
61 if new_value > 1:
62 new_value = 0
63
64 self.progressbar.props.fraction = new_value
65
66 # As this is a timeout function, return True so that it
67 # continues to get called
68 return True
69
70
71def on_activate(app):
72 win = ProgressBarWindow(application=app)
73 win.present()
74
75
76app = Gtk.Application(application_id='com.example.App')
77app.connect('activate', on_activate)
78
79app.run(None)